Description
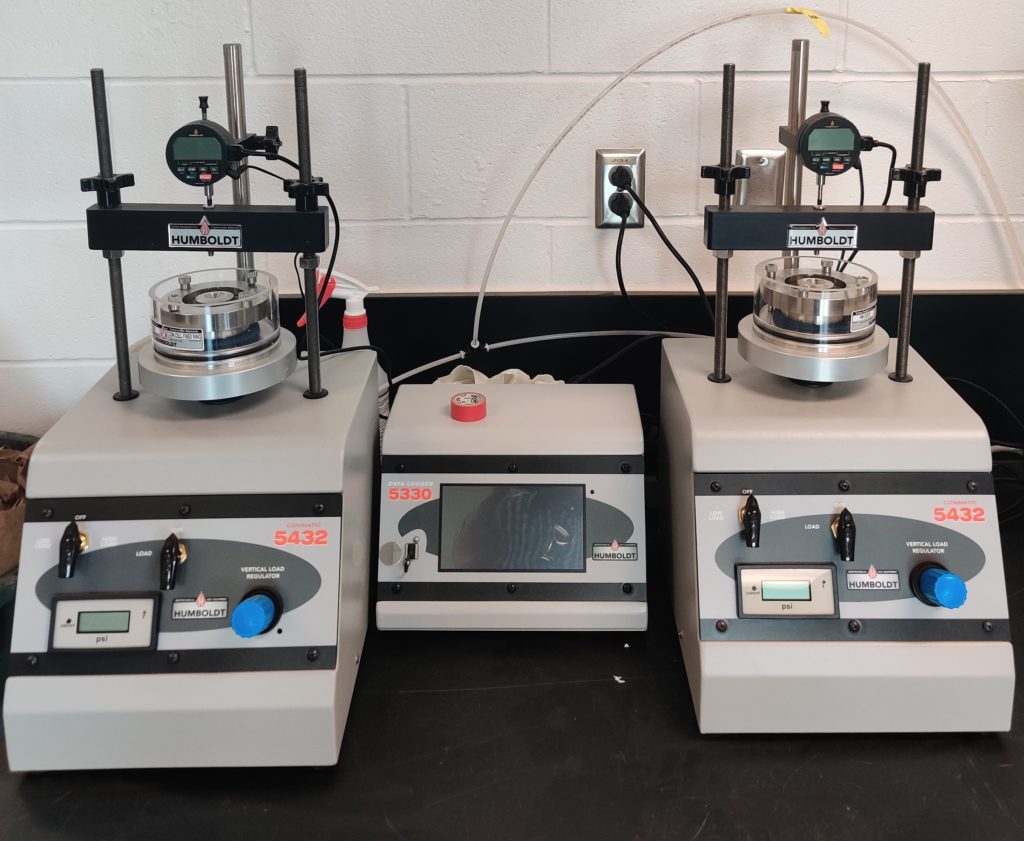
This consolidation setup can be used to perform 1D consolidation using incremental loading (ASTM D2435, AASTHO T216, BS:1377:5), 1D-swell or collapse of soils (ASTM D4546). This device is capable of applying instant load without impact for a stress-controlled consolidation. The system uses air pressure for applying stresses to the sample and a dial gauge to measure the deformation.
Testing Ranges
This test helps to determine parameters that can be used to estimate both magnitude and time rate of settlement using conventional consolidation theory by Terzaghi.
Testing can be done at two different load settings making the device sensitive to small loads as well.
- High Load –1 to 32 tsf
- Low Load – up to 1 tsf
Max sample size = 4” (100mm)
Maximum load = 2200 lbf (10 kN)
Dimensions = 12” x 12” x 30”
Material Properties
Consolidation Properties
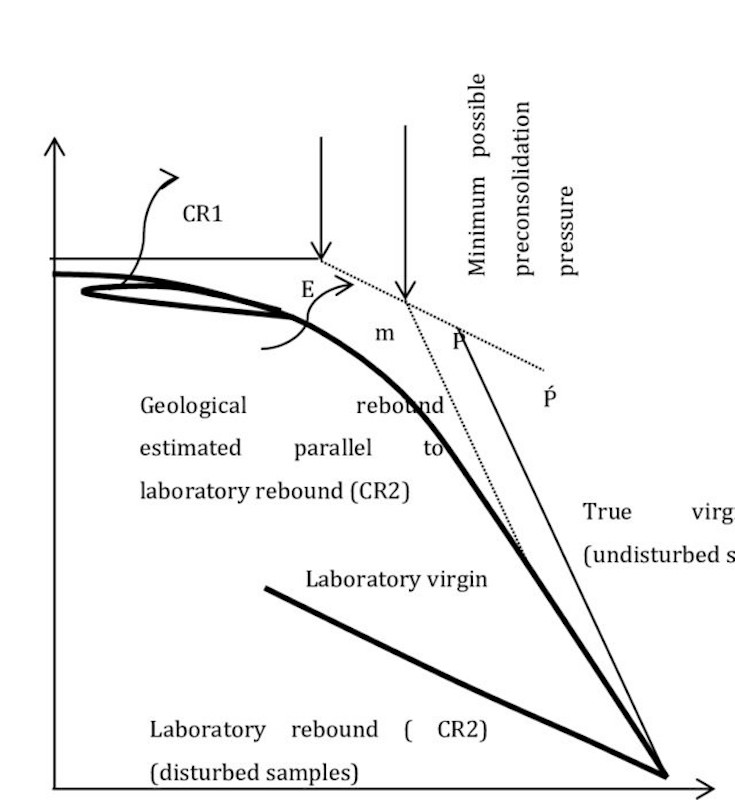
- Preconsolidation pressure, σ’p
- The overburden stress that marks the boundary between NC (loose) and OC (dense) deformation response of a soil to loading
- Usually indicative of past pressure experienced by the soil from glaciers or eroded layers
- Recompression Index, CR = Δe/Δlog(σ’v)
- Indicates the behavior of soil volume change under loads less than the preconsolidation pressure.
- It could also be used to approximate swelling due to unloading.
- Compression Index, CC = Δe/Δlog(σ’v)
- Indicates the change of soil volume under loads greater than the preconsolidation pressure
- Duration of Primary Consolidation, tp
- Secondary Compression Index, Cα = Δe/Δlog t
- Indicates the change of soil volume under a constant loading
Swell Properties
- Swell pressure (σ’s), Swell strain
Field Application
- Estimation of foundation settlement.
- Design and analysis of soft ground.
- Analysis of settlement characteristics of landfill.
- Design of road pavement for expansive soils.
Publications
- He, Shi, Xinbao Yu, Aritra Banerjee, and Anand J. Puppala. “Expansive soil treatment with liquid ionic soil stabilizer.” Transportation Research Record 2672, no. 52 (2018): 185-194.
- Pedarla, Aravind, Anand J. Puppala, Laureano R. Hoyos, and Bhaskar Chittoori. “Evaluation of swell behavior of expansive clays from internal specific surface and pore size distribution.” Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering142, no. 2 (2016): 04015080.
- Pedarla, Aravind, Anand J. Puppala, Ujwalkumar D. Patil, Laureano R. Hoyos, and Alejandro H. Pino. “A Semi-empirical Approach-Based Model for Swell Characterization of Expansive Clays.” Geotechnical and Geological Engineering37, no. 6 (2019): 5371-5381.
- Puppala, Anand J., Surya SC Congress, Nagasreenivasu Talluri, and Ekarin Wattanasanthicharoen. “Sulfate-heaving studies on chemically treated sulfate-rich geomaterials.” Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 31, no. 6 (2019): 04019076.
- Puppala, Anand J., Aravind Pedarla, Laureano R. Hoyos, Claudia Zapata, and Tejo V. Bheemasetti. “A semi-empirical swell prediction model formulated from ‘clay mineralogy and unsaturated soil’properties.” Engineering geology 200 (2016): 114-121.
- Puppala, Anand J., Sireesh Saride, Raja V. Yenigalla, Bhaskar CS Chittoori, and Ekarut Archeewa. “Long-term performance of a highway embankment built with lightweight aggregates.” Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities 31, no. 5 (2017): 04017042.
- Samuel, Rinu, Oscar Huang, Aritra Banerjee, Anand Puppala, Jasaswee Das, and Miladin Radovic. “Case Study: Use of Geopolymers to Evaluate the Swell-Shrink Behavior of Native Clay in North Texas.” In Geo-Congress 2019: Soil Improvement, pp. 167-178. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2019.
- Cai, Guojun, Songyu Liu, and Anand J. Puppala. “Consolidation parameters interpretation of CPTU dissipation data based on strain path theory for soft Jiangsu quaternary clays.” Marine Georesources & Geotechnology 33, no. 4 (2015): 310-319.
- Sekhar Madhyannapu, Raja, Madhira R. Madhav, Anand J. Puppala, and A. Ghosh. “Compressibility and collapsibility characteristics of sedimented fly ash beds.” Journal of materials in civil engineering 20, no. 6 (2008): 401-409.