Description
Terrestrial laser scanning (TLS), also referred to as terrestrial LiDAR (light detection and ranging) or topographic LiDAR, acquires XYZ coordinates of numerous points on land by emitting laser pulses toward these points and measuring the distance from the device to the target. During the data acquisition process, a set of data points, referred to as a point cloud, is generated in 3D space. Based on the unabsorbed wavelength of laser light at each point on the surface, physical features of target points, such as distance, color, and reflective intensity, can be recorded. For pavement forensic analysis, a scan point density of 0.03 m (0.1 ft) or less is required for a distance of 38.1 m (125 ft) from the scanner
Equipment Specifications
Faro Laser Scanner FOCUS3D X 330. Scanning of target up to 330 m can be performed. Integrated with GPS receivers, Altimeters, dual axis compensators, WiFi
Ranging Unit
Unambiguity Interval: By 122 till 488 Kpts/sec at 614m; by 976 Kpts/sec at 307m
Range Focus3D X 330: 0.6m – 330m indoor or outdoor with upright incidence to a 90% reflective surface
Measurement Speed (pts/sec): 122,000 / 244,000 / 488,000 / 976,000
Ranging Error: ±2mm
Color Unit
Resolution: Up to 70 megapixel color
Dynamic Color Feature: Automatic adaption of brightness
Parallax: Co-axial design
Deflection Unit
Vertical Field of View (vertical/horizontal): 300° / 360°
Step Size (vertical/horizontal): 0.009° (40,960 3D-Pixel on 360°) / 0.009° (40,960 3D-Pixel on 360°)
Max. Vertical Scan Speed: 5,820rpm or 97Hz
Laser (Optical Transmitter)
Laser Class: Laser class 1
Wavelength: 1550nm
Beam Divergence: Typical 0.19mrad (0.011°) (1/e, halfangle)
Beam Diameter at Exit: Typical 2.25mm (1/e)
Field Applications
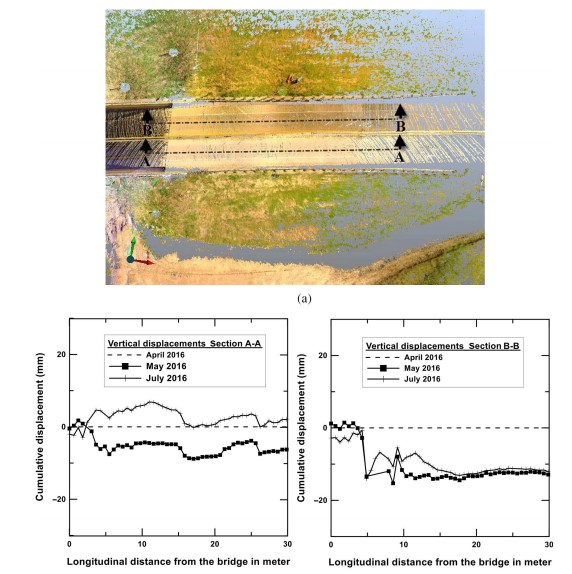
Assess the performance of
- Bridge infrastructures
- Embankments
- Bridge decks
- Abutments
- Column supported on drilled shaft
Publications
- Shafikani, Ali, Tejo V. Bheemasetti, and Anand J. Puppala. “Performance Evaluation of a Bridge Infrastructure Using Terrestrial Laser Scanning Technology.” Geotechnical Testing Journal 42, no. 6 (2019): 1587-1605.
- Shafikhani, A. (2018). A NEW APPROACH FOR PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF BRIDGE INFRASTRUCTURE USING TERRESTRIAL LIDAR AND ADVANCED MATHEMATICAL MODELING (Doctoral dissertation).